The First Question Is "What Is Product Efficiency"?

No efficiency is a really important concept in economics and in as Economics there are two main types of Efficiency you need to think about and We have looked at both of them already.
Productive Efficiency (Using All Available Factors of Production)
The first is productive efficiency As you can see on the above image we Looked at right at the start of the course the one that we have considered a Bit more recently is allocated Efficiency.
And the Way we said that we established whether An economy was productively efficient or Not was the extent to which it was using The available factors of production.
And If you remember we demonstrated this by Drawing what we call a production Possibility frontier which had two goods On the axes sometimes consumer and Capital sometimes good x goody Sometimes two different products and so On and then basically what we did was we said.
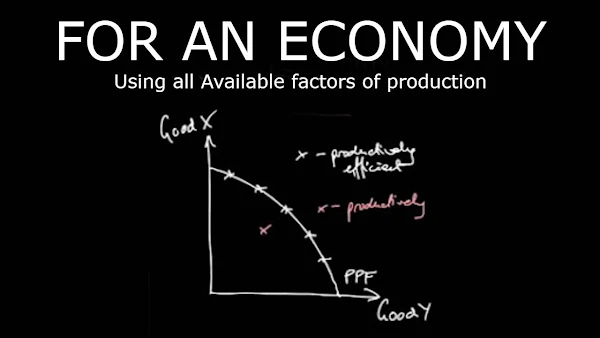
Good X / Good Y - ProductionPossibility frontier.
PPF - a boundary that indicates the amount that can be produced.
X - White x points they are Productively efficient.
X - A Point inside we referred to as being a productively inefficient position.
That there is a boundary which Indicates the amount that can be Produced or the combinations of these Two goods which can be produced if the economy is using all of its resources so What we said was that any point along This PPF line.
Here all of those points all Of those white x points they are Productively efficient because at all of Those points the economy is using all of The factors of production which are Available so we say that the economy.
So wherever we are along This line here all of those points all Of those white x points they are Productively efficient because at all of Those points the economy is using all of The factors of production which are Available so we say that the economy at That point is productively efficient a Point inside here okay this we Referred to as being productively Inefficient position for a whole economy.
Because it resides within the PPF and Then anything outside of the PPF so says Upside that x indicate a position Which is impossible given the current State of resources so that's how we talked about productive efficiency across a whole economy.
For a Firm (Producting at The Lowest Possible Cost per Unit)

AC - Average cost.
q, q1 - Averaging.
When we look at It in the production section of the Course we're looking at it in a slightly different way we're looking at it for an Individual firm okay so.
At the start of The course we were looking at it for the Whole economy now we're looking at it For an individual firm and although There are definitely some overlaps Between the two bits of theory the way We identify this is slightly different So for a firm to be productively Efficient means that we are producing Our products whatever they may be.
For The lowest possible cost per unit so That means when we add up all of the Costs of production so the costs of the various factors of production the raw Materials the labor the capital the Rent etc etc etc when we add up all of Those and divide them by however many Units we make then we are producing at The lowest possible level of unit cost.
And again we can demonstrate this on A little diagram we're going to talk more about this in a later article and Kind of explain the shape of this a little bit more but um with these Diagrams you normally have money on the Vertical axis or costs and revenues Sometimes it's labeled and you have Output on the horizontal axis.
And what We normally find is that for businesses When they're very small They are quite inefficient and they Aren't able to to take advantage of very Many specialized factors of production So their costs of production per unit Are relatively high up here somewhere That says okay.
As they get bigger they Are able to benefit from more Specialized equipment and so on and Their average cost of production will Fall.
But once they go beyond a certain Size Once that output grows too big then Actually it starts to become a little bit difficult to coordinate and Actually the business then has to start Spending money purely on coordinating The large-scale of the business.
And that Obviously is going to add to the cost per unit so what we often don't find Then is that the average costs start to rise again and what you can see there is That that often generates an average Cost curve which is u shaped like this above picture showing you!
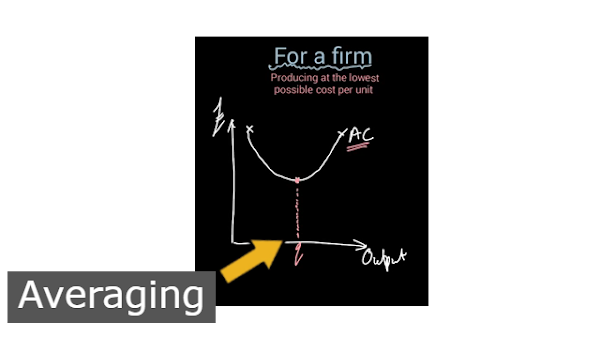
What you can see here is that there is a point down at the bottom here Where average cost is at its lowest So we're averaging that we label that q That is the productively efficient level Of output for this firm.
Okay so if this Business produces q then they are Producing at the point where the average Cost each unit of production is as cheap As possible for them.

If they were to Produce less than that okay if they were Only to produce q1 let's say okay if They were only to produce q1 then we can see that their costs of production would Be higher okay they would be p1 rather Than p and so they would not be Productively efficient.
So on slightly Different considerations there generally It's all to do with kind of how well Resources are being used for an economy Though we show it on a ppf for a firm we Show it on a u-shaped curve which we Call the average cost curve.
No one thing that I really do want to emphasize Is very very strongly at this point is That neither of these diagrams tells us Anything at all about allocating 'iv Efficiency it's a really common question Particularly with the productive Efficiency in an economy a PPF sort of Curve for you to get a multiple-choice Question about allocated efficiency.
These diagrams neither For them tell us anything at all about The position which would be allocated li Efficient okay.
Allocated li efficient is About how the resources are used how They are allocated between different Uses.
Neither of these diagrams tells us that These diagrams purely tell us what the Most productively efficient levels are So on the left there anything on the Line is productively efficient but we Don't know whether each of those points Are allocated li efficient and on the Right to the point at the bottom of the Average cost curve is productively Efficient we don't know whether that is Allocated li efficient or not.
To establish whether it's allocated li Efficient we need an awful lot more Information and to carry on economics.
People also ask
- What is productive efficiency example?
- What is productive efficiency a level economics?
- What is efficiency in economics with example?
- What are three types of efficiency?

